ExeOutput for PHP allows you to localize your application, translating built-in text and creating multilingual interfaces. This means that dialog captions, button labels, and other interface elements can be displayed in any language you choose. This section explains how to manage your application’s text strings and use language files.
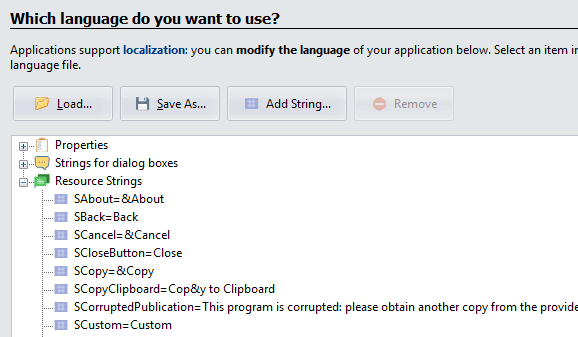
Resource Strings #
Resource strings are named text constants used to translate UI elements like messages, menus, buttons, and window titles. For example, to create a French and English version of your application, you don’t need to create two separate versions. Instead, you can define a list of resource strings for each language.
In the ExeOutput for PHP user interface (for example, in button captions), you can reference a resource string by wrapping its name in percent signs: %SAbout%. At runtime, the application replaces these identifiers with the string value for the currently selected language.
Managing Resource Strings #
- To edit a string, select it from the list to open the editor. Modify the Value field and click Apply to save your changes.
- To add a new string, click Add String. You will be prompted for a name, which must be unique, start with an
S, and contain only alphanumeric characters. - To remove a string, select it and click Remove. You can only remove custom strings that you have added.

Using Resource Strings in Code #
You can access resource strings directly from your code:
PHP: Use the built-in
exo_get_resstringfunction:<?php echo exo_get_resstring('SPubCopyright'); ?>HTML/JavaScript: Use the asynchronous
exeoutput.GetStringfunction, which returns the value to a callback:<div id="demo"></div> <script> function displayString(content) { document.getElementById('demo').innerHTML = '<p>' + content + '</p>'; } exeoutput.GetString("SPubCopyright", displayString); </script>
System Page Strings #
These special strings are used exclusively for translating the content of built-in system dialog boxes.
They are referenced using the syntax [#ID], where the ID typically starts with a Y (for example, [#YAbout]). Unlike resource strings, these are not available at runtime. They are compile-time constants; ExeOutput for PHP replaces the [#ID] placeholders with their values when the application is built.
You can edit these strings in the same way as regular resource strings.
Managing Language Files #
You can import and export all of your project’s strings to and from language files (.exol extension) using the Load and Save buttons. This allows you to reuse translations across multiple projects or share them with other developers.
- All strings are saved directly within the project file (
.exop), so you do not need to keep a separate language file for each project. - If you plan to distribute a language file, be sure to fill out its properties. The locale is the numeric Windows Language Code Identifier (LCID). You can find a list of these identifiers on the Microsoft website.
- You can set a default language file in the Environment Options to have it automatically loaded every time you create a new project.
Automatic Resource Strings #
ExeOutput for PHP automatically creates several resource strings at compile time based on your project settings. These can be used in your code just like any other resource string.
SPubTitle: The title of your application.SPubHomepage: The default homepage URL.SPubAuthor: The author’s name.SPubCopyright: The copyright notice for your application.SPubEMail: The author’s email address.SPubVersion: The application’s file version.SPubProductVer: The application’s product version.



